History: 76 yo male with abdominal pain.
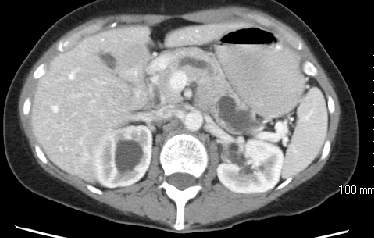
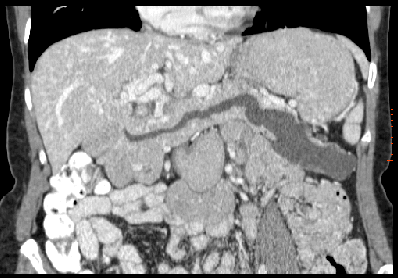
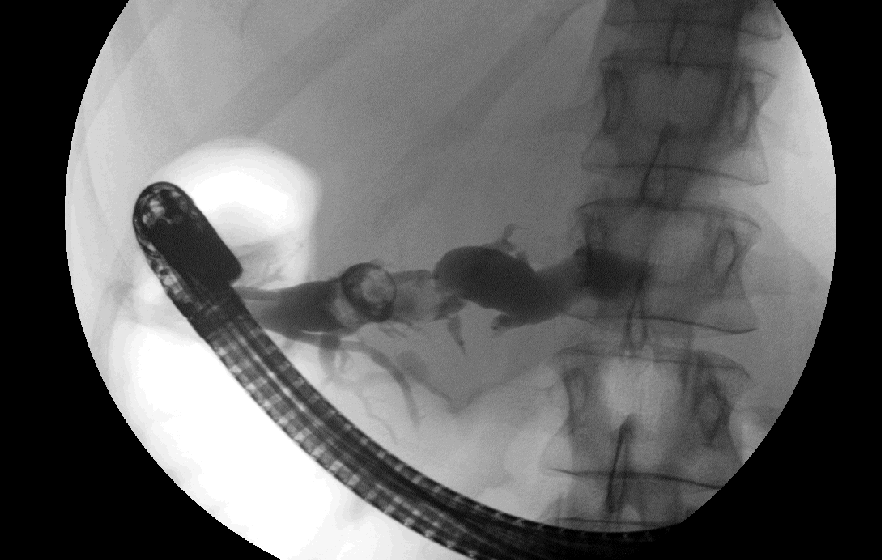
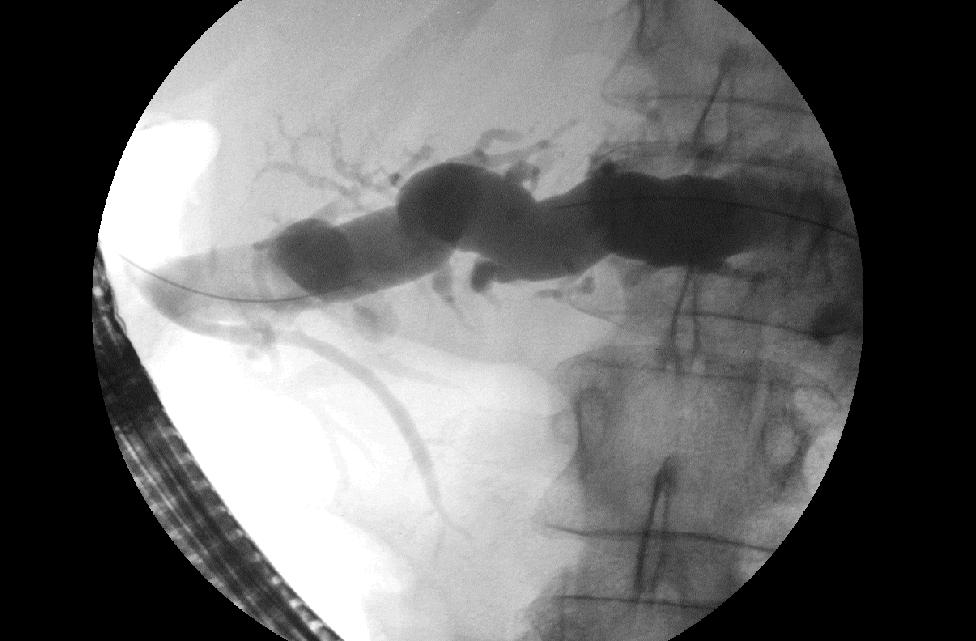
Solution: Intraductal papillary mucinous tumor (IPMT) is a tumor that can occur in either the main pancreatic duct, or side branch ducts. It is on a spectrum from benign to low grade malignancy and arises from the epithelial lining. Symptoms are often secondary to the excessive mucin production. The findings of this case are very characteristic of the main duct type with dilatation and tortuosity of the main duct of the pancreas with filling of the duct with cystic material (mucin) which is confirmed on the ERCP images. Most common presenting features are pain, weight loss, diarrhea, pancreatitis and diabetes. There was an excellent review in Radiology (December 2000 Radiology, 217, 757-764) on this subject where they determined that "the most specific predictive signs of malignancy were presence of diabetes and, at CT, a solid mass, main pancreatic duct dilatation greater than 10 mm, diffuse or multifocal involvement, and attenuating or calcified intraluminal content." Since the pancreatic duct in this case was greater than 1 cm in diameter, there is concern for malignancy. Treatment is surgical and the prognosis depends on the ultimate histology and invasiveness of the tumor.