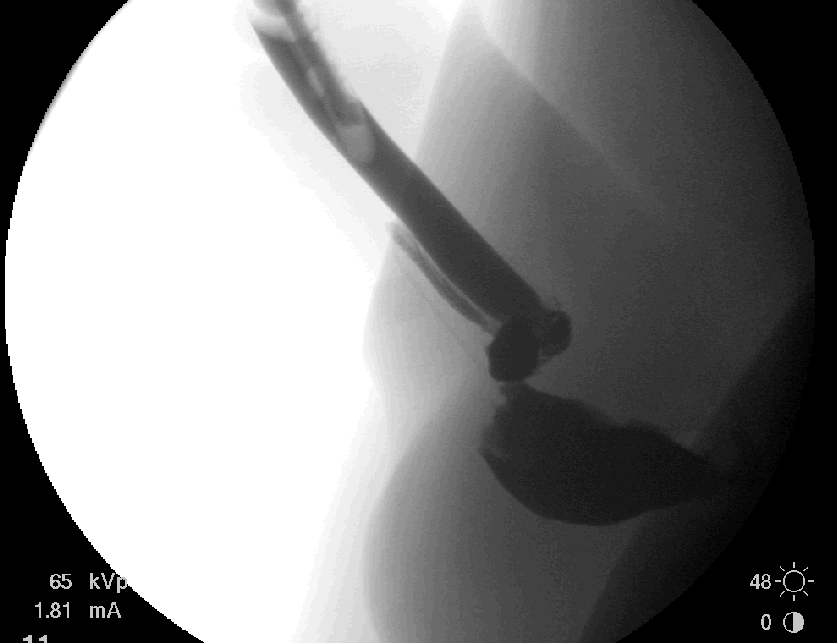
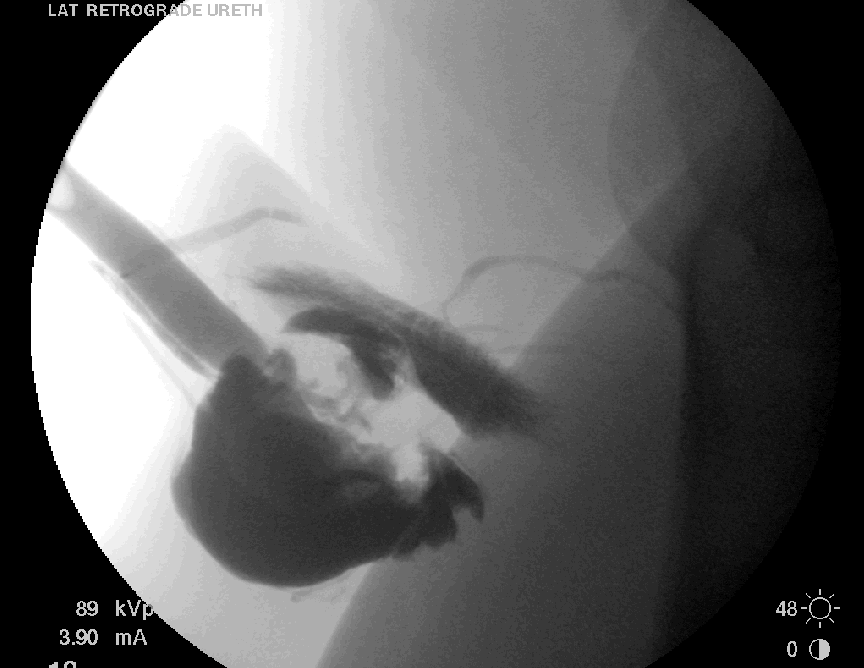
History: 23 yo male s/p MVA
Solution: The retrograde urethrogram in this case shows a normal penile urethra, but severe irregularity of the bulbous and membranous urethra with extravasation of contrast into the adjacent soft tissues and no filling of the urinary bladder. There is also evidence of intravasation of contrast into the venous system. Overall, the findings are most consistent with a complete urethral disruption at the level of the membranous urethra. These injuries are usually defined as either posterior (membranous and prostatic urethera) and anterior (distal to the membranous urethra). Posterior urethral injuries are usually associated with pelvic fractures while anterior urethral injuries such as this one are not. These are often treated with suprapubic catheter and delayed repair, but can attempt immediate repair with interlocking sounds or other techniques depending on the severity of other injuries.