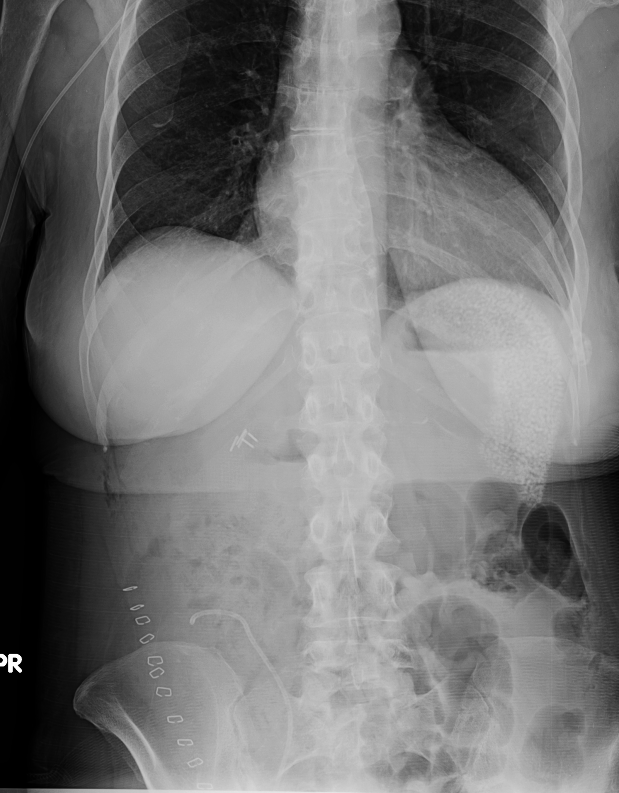
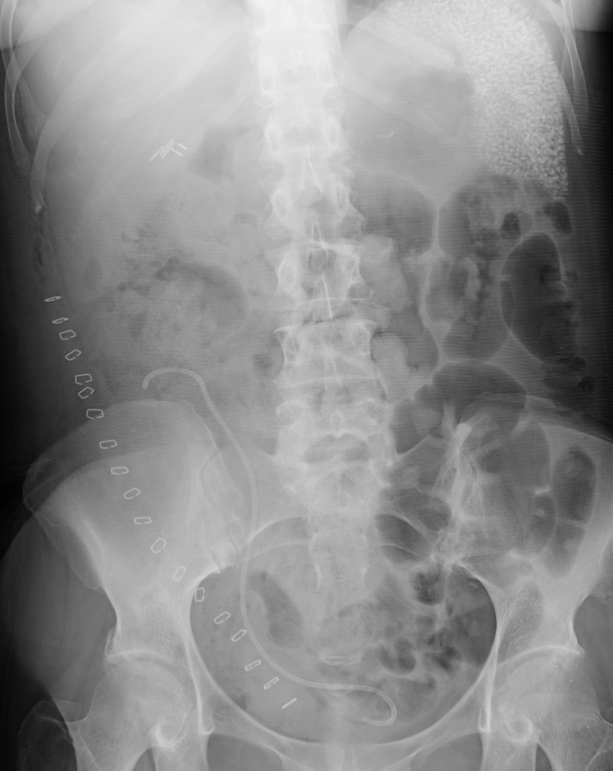
History: 54 yo female s/p kidney transplant. ? retained instruments or sponges.
Solution: The differential diagnosis for splenic calcifications is broad and includes, primarily infectious and post-infectious causes, as well as traumatic causes, infarctions, and exposure to thoratrast. However, the pattern seen in this patient is different than what is typically seen and is somewhat characteristic of the rounded calcifications seen in the setting of lupus (the reason for the patients renal disease and need for a transplant). These have been described as larger than typically seen with OGD, diffuse, but sparing the immediate subcapsular spleen, and although infrequently seen even with lupus, this appearance is somewhat typical when it occurs. Exact etiology is not clear, but seems to be a visceral vasculitic manifestation that is generally asymptomatic, doesn't need treatment and doesn't really seem to reflect how severe the disease is. Here are some CT images of these calcifications.