History: 12 yo male with dysphagia
Solution: Dysphagia Lusoria Caused by an Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery.
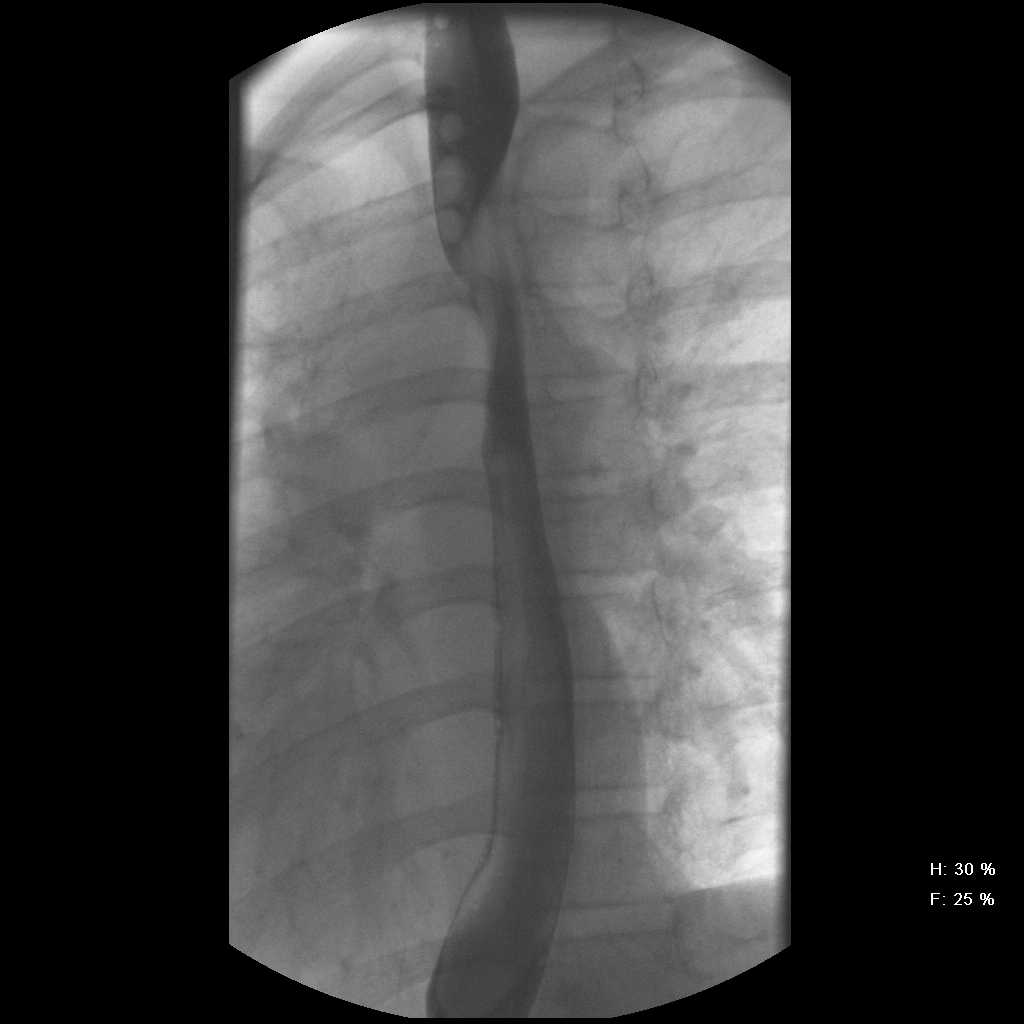
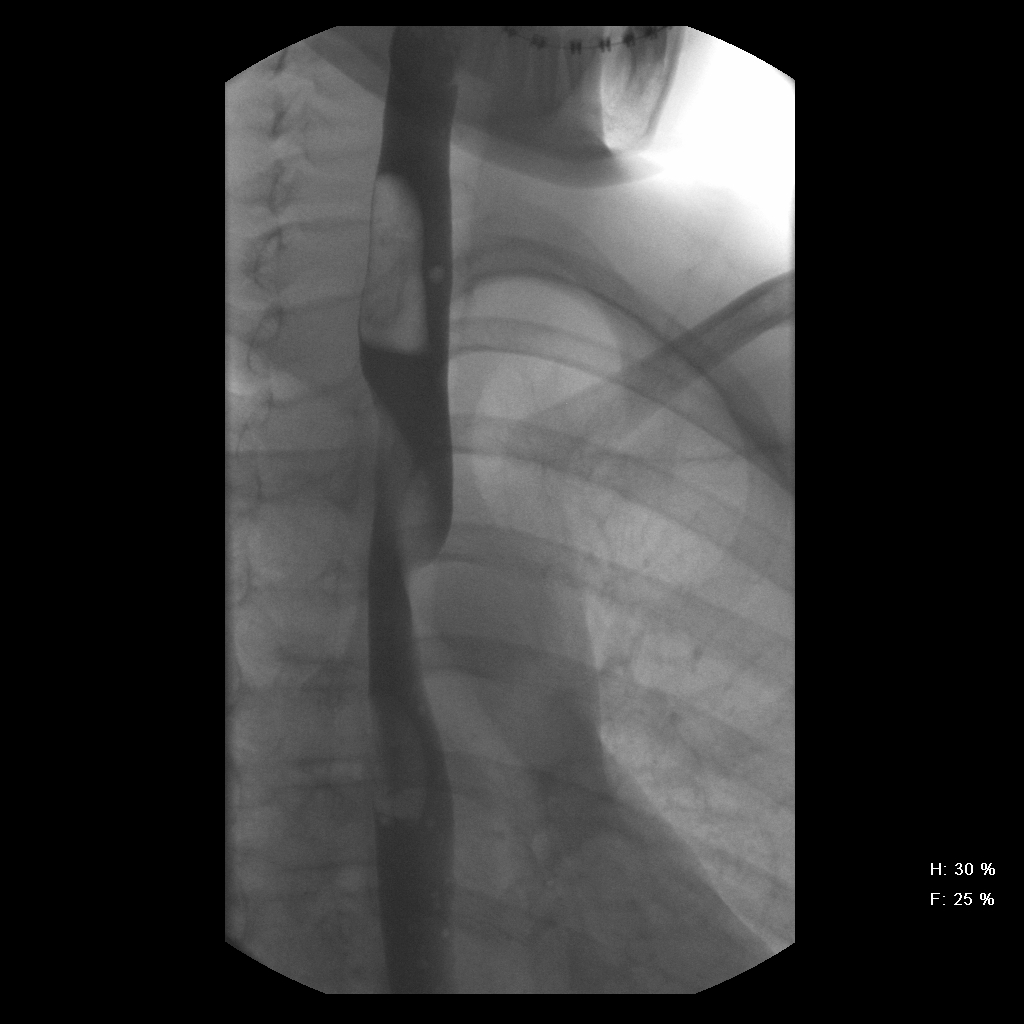
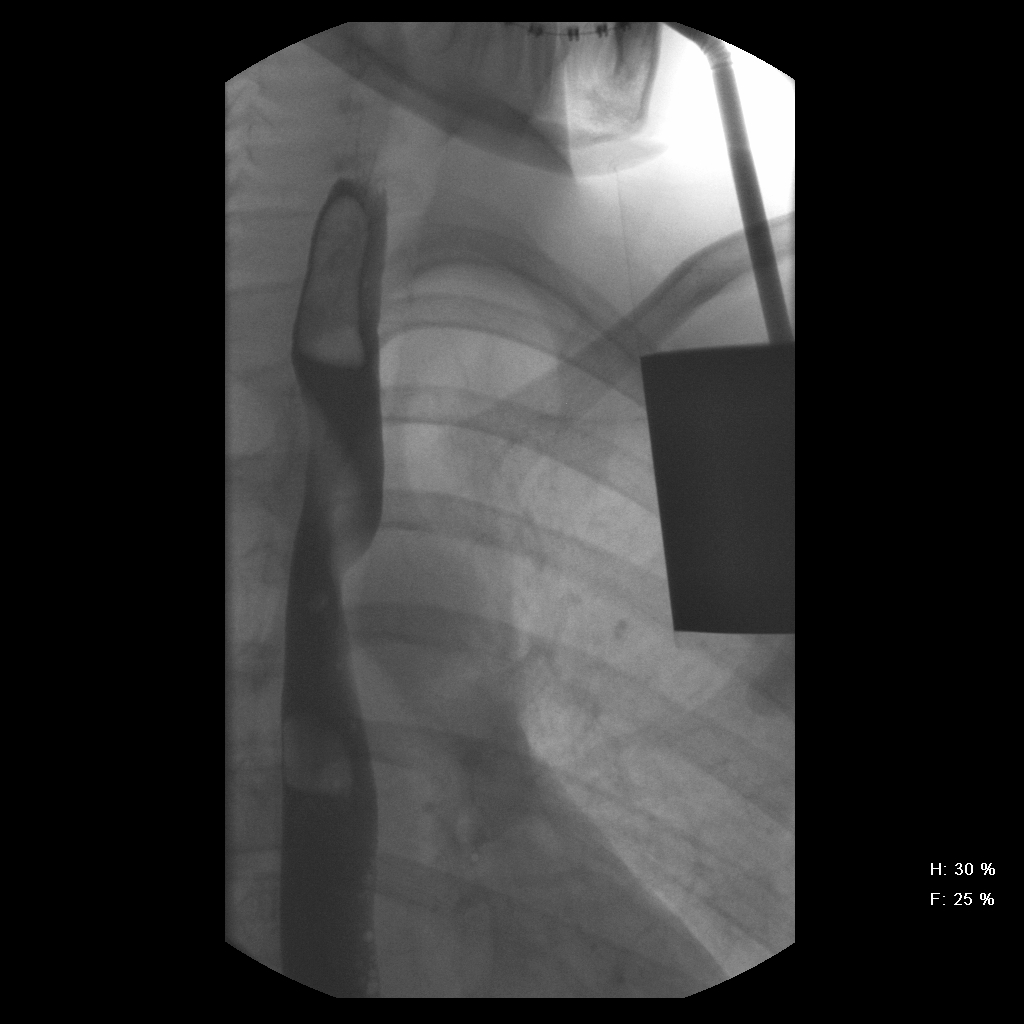
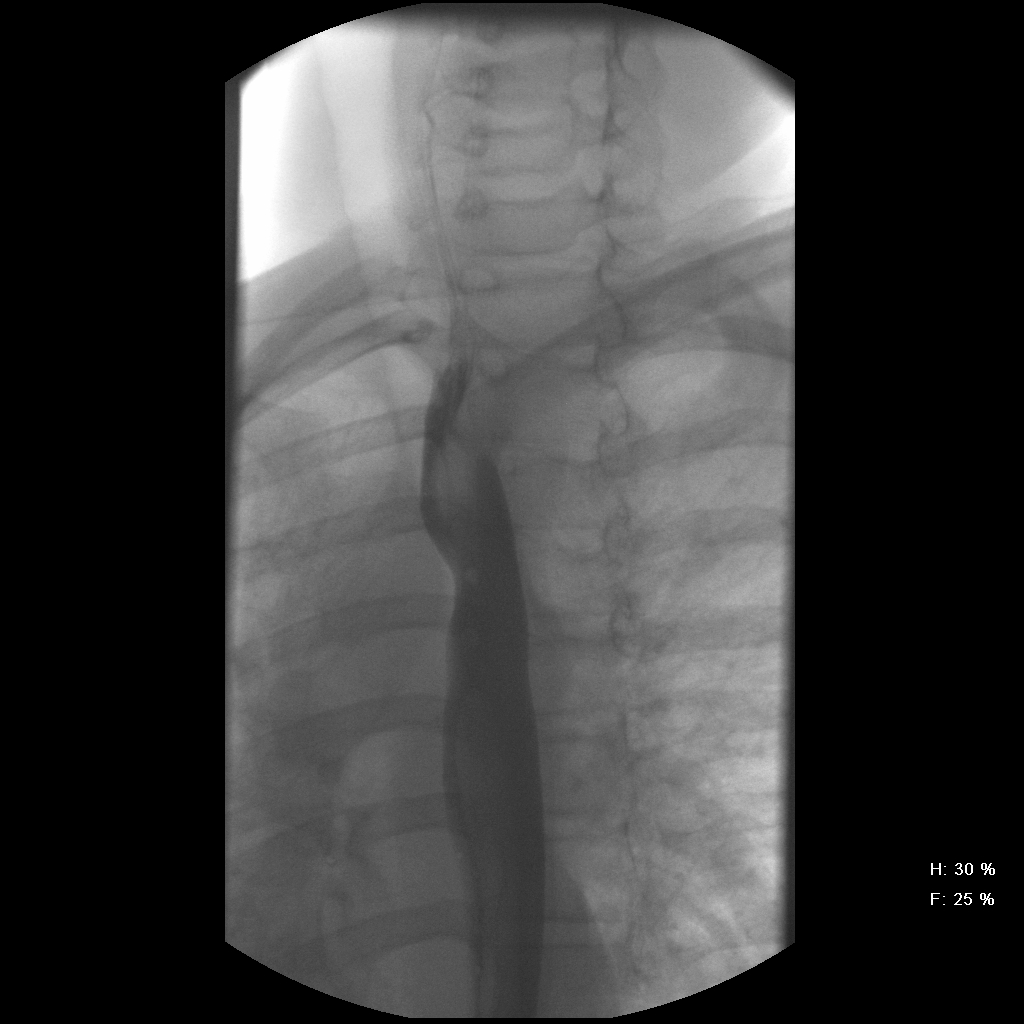
The most common embryologic abnormality of the aortic arch is an aberrant right subclavian artery, which occurs in 0.5% to 1.8% of the population. Most cases are asymptomatic, but if there is compression of the esophagus, dysphagia can develop. This is often referred to as dysphagia lusoria, which means dysphagia from a \"freak of nature\". In this case, the esophagogram reveals an oblique extrinsic defect with an inferior-to-superior (left-to-right) course essentially diagnostic of an aberrant right subclavian artery. An arteriogram (conventional, CT, or MR) will confirm the aberrant origin of the right subclavian artery, arising from the aorta distal to the usual left subclavian artery. The artery has a retro-esophageal course that can cause compression of the esophagus.
If the symptoms are progressive or severe enough surgical correction will be performed.
The most common embryologic abnormality of the aortic arch is an aberrant right subclavian artery, which occurs in 0.5% to 1.8% of the population. Most cases are asymptomatic, but if there is compression of the esophagus, dysphagia can develop. This is often referred to as dysphagia lusoria, which means dysphagia from a \"freak of nature\". In this case, the esophagogram reveals an oblique extrinsic defect with an inferior-to-superior (left-to-right) course essentially diagnostic of an aberrant right subclavian artery. An arteriogram (conventional, CT, or MR) will confirm the aberrant origin of the right subclavian artery, arising from the aorta distal to the usual left subclavian artery. The artery has a retro-esophageal course that can cause compression of the esophagus.
If the symptoms are progressive or severe enough surgical correction will be performed.