History: 35 yo male presents to emergency room with acute right pelvic pain.
Solution: Epiploic appendigitis
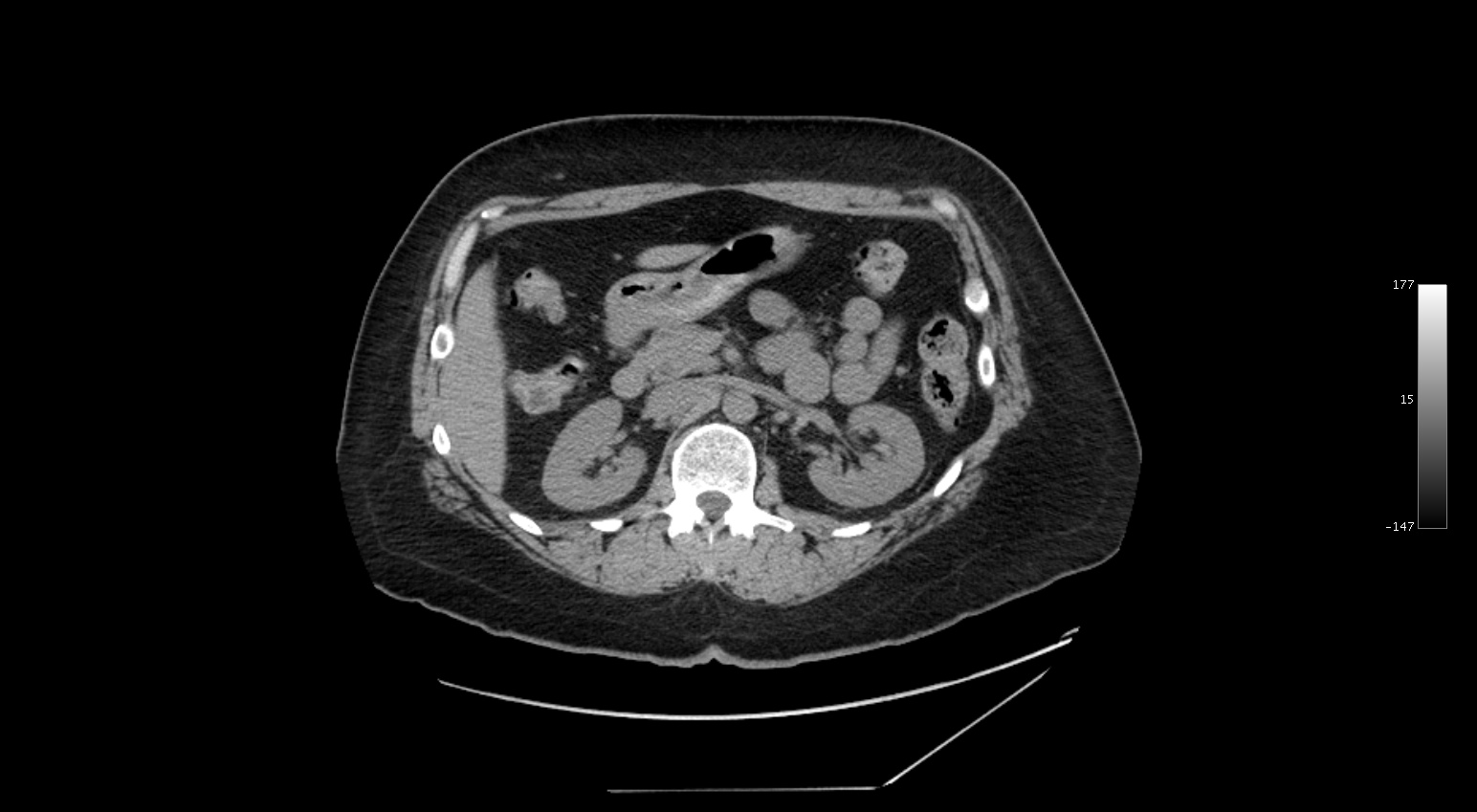
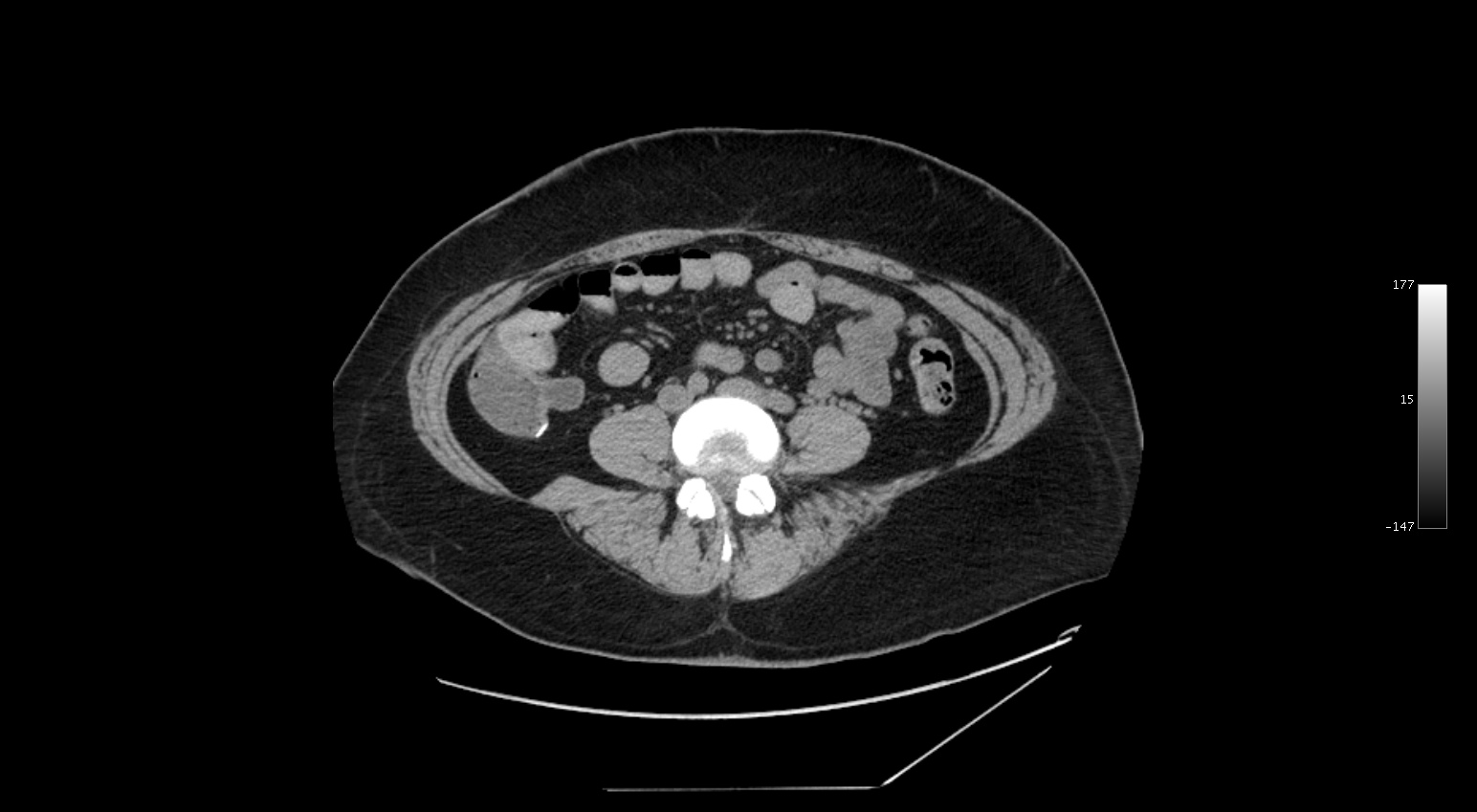
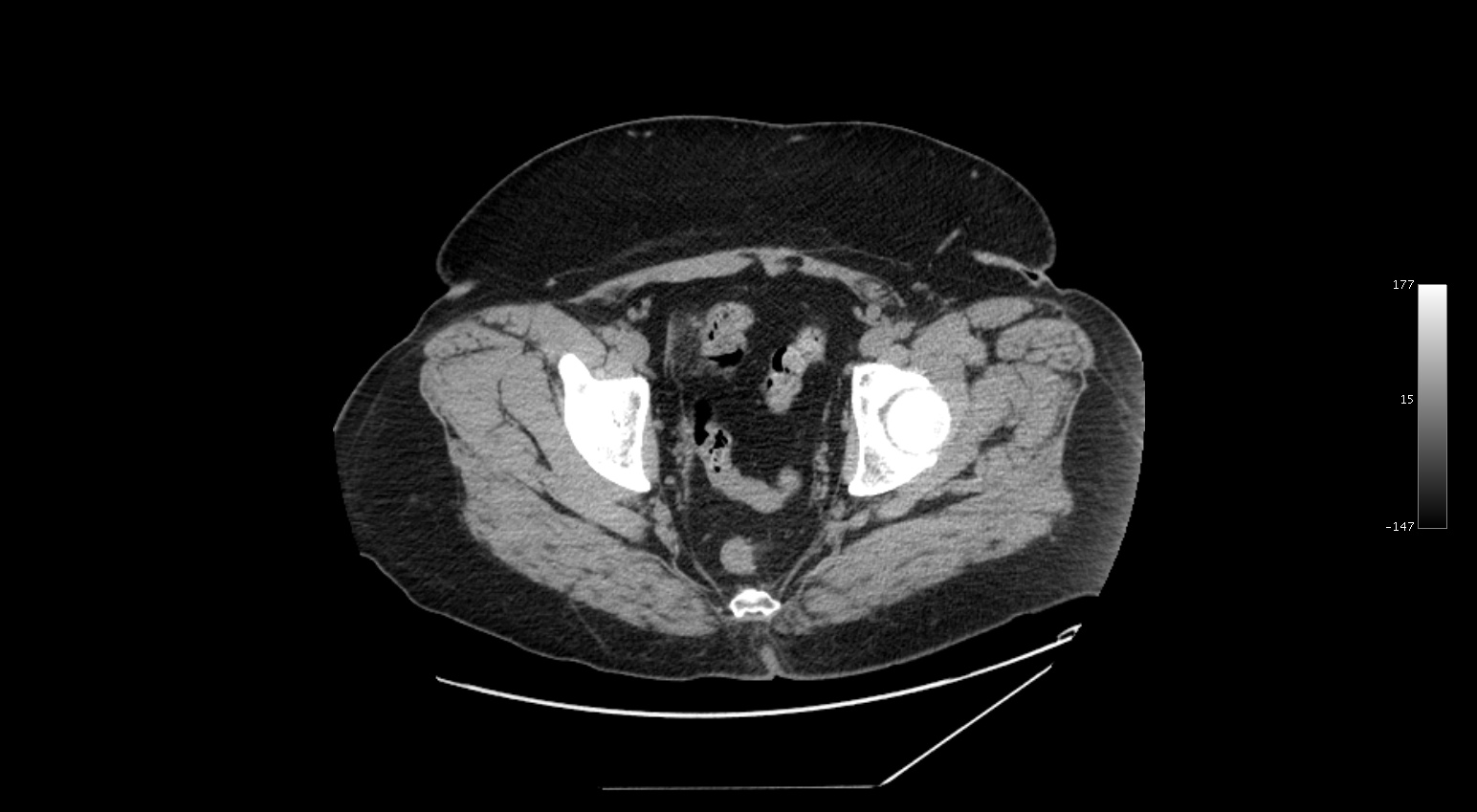
The findings in this case (CT flank pain) include: Post-surgical changes at the cecal base indicative of previous appendectomy, normal kidneys with no kidney stones, and an area of inflammation centered in the mesenteric fat adjacent to the sigmoid colon. Although this condition is described as being rare, it is likely more common than is realized and the reason it is being identified and diagnosed more now is likely related to improvements in imaging, rather than an increase in incidence.
It is a torsion of an epiploic appendage of the colon and represents a fatty infarct related to vascular compromise to the appendage. Symptoms generally include abrupt onset of abdominal pain that resolves WITHOUT intervention over 5-7 days.
The finding on CT is a fat attenuation mass with inflammatory stranding and a hyperattenuating rim. If you identify this finding, the patient should be managed conservatively.
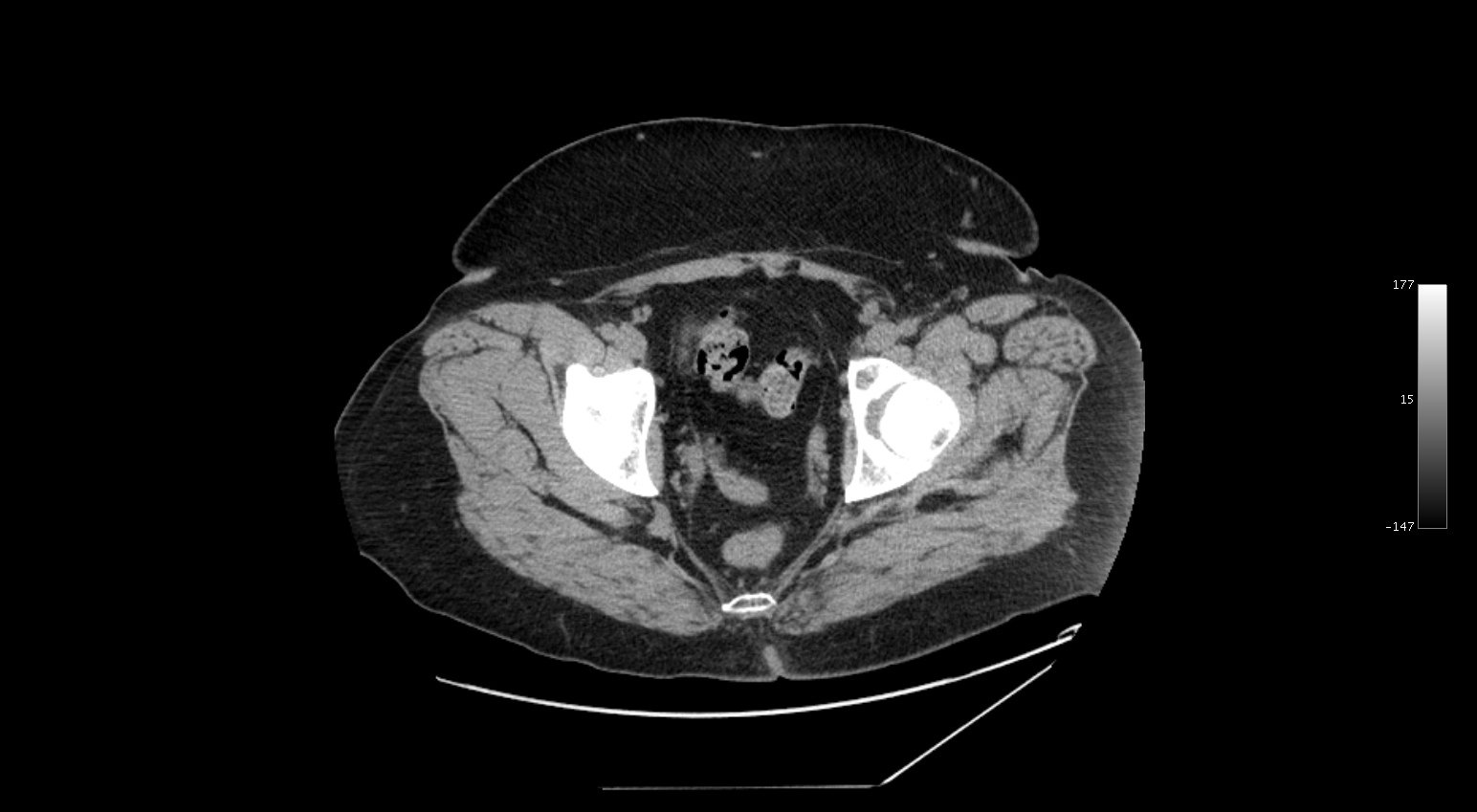
The findings in this case (CT flank pain) include: Post-surgical changes at the cecal base indicative of previous appendectomy, normal kidneys with no kidney stones, and an area of inflammation centered in the mesenteric fat adjacent to the sigmoid colon. Although this condition is described as being rare, it is likely more common than is realized and the reason it is being identified and diagnosed more now is likely related to improvements in imaging, rather than an increase in incidence.
It is a torsion of an epiploic appendage of the colon and represents a fatty infarct related to vascular compromise to the appendage. Symptoms generally include abrupt onset of abdominal pain that resolves WITHOUT intervention over 5-7 days.
The finding on CT is a fat attenuation mass with inflammatory stranding and a hyperattenuating rim. If you identify this finding, the patient should be managed conservatively.